Blended learning is reshaping the landscape of modern education by combining traditional face-to-face instruction with digital tools. This approach not only leverages the strengths of both methods but also adapts to the diverse needs of today’s learners. As schools and universities increasingly adopt blended learning, it’s clear that this model offers flexibility and engagement that purely traditional or purely online approaches cannot provide.
Blended learning theory is based on the idea of integrating in-person teaching with online components to create a comprehensive learning experience. It allows students to access course materials, collaborate with peers, and receive instruction both in class and virtually. The theory emphasizes flexibility and personalized learning, helping students take ownership of their educational journey.
The evolution of technology has made blended learning more accessible and effective. By combining direct instruction with digital resources, students can explore content more deeply and at their own pace. Educators play a critical role in guiding this process, ensuring that the balance between online and offline learning is optimized for student success.
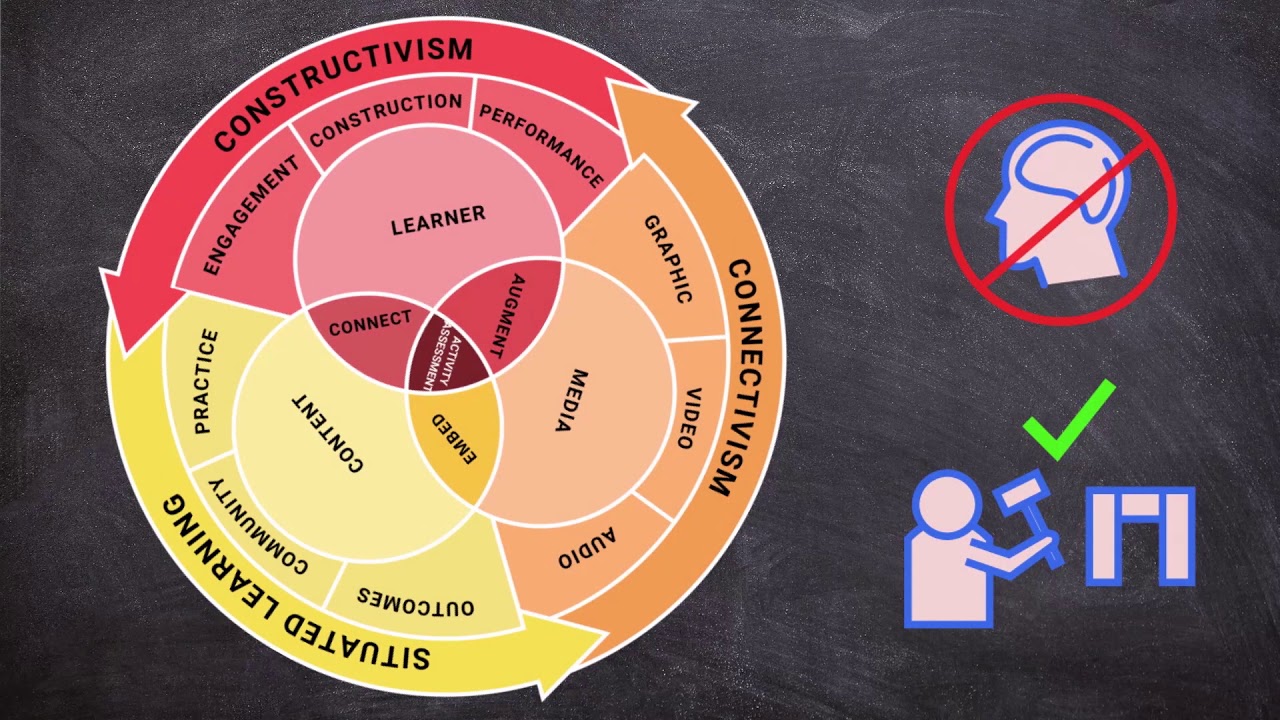
Core Components of Blended Learning
Blended learning is built on several key components that, when combined, create a rich and flexible educational experience. These components include online learning integration, face-to-face instruction, and a student-centered approach. By focusing on these core elements, educators can provide students with a more personalized and adaptive learning journey.
Online Learning Integration
Online learning integration is a central aspect of blended learning. It involves incorporating digital tools and platforms to enhance the traditional classroom environment. In this model, students have access to online resources such as videos, assignments, and interactive tools, allowing them to engage with the material beyond the physical classroom.
- Flexibility: Students can review materials at their own pace and revisit lessons if they need additional clarification.
- Accessibility: Digital resources are accessible anytime, from anywhere, which is especially useful for students who may face challenges attending in-person classes.
- Collaboration: Many online platforms encourage peer interaction through discussion forums and group projects, fostering a sense of community even in a virtual setting.
The integration of online learning not only expands access to education but also promotes independent learning. Students have more control over their learning process, which can lead to improved outcomes and deeper engagement with the content.
Face-to-Face Instruction
Face-to-face instruction remains an essential component of blended learning. It provides direct interaction between teachers and students, which is critical for fostering relationships and ensuring personalized guidance. In-person sessions allow for real-time feedback, adjustments to teaching strategies, and immediate clarification of complex concepts.
- Personalized Attention: Teachers can identify students’ strengths and weaknesses and offer tailored support.
- Engagement: Classroom activities such as group discussions, hands-on experiments, and interactive lessons help maintain student interest.
- Social Interaction: Face-to-face learning encourages peer communication and collaboration, helping students develop social skills that are vital for personal growth.
While online components offer flexibility, face-to-face instruction ensures that students still benefit from the human connection that is so important in education.
Student-Centered Approach
In blended learning, the student-centered approach is crucial. This means that learning is tailored to the individual needs, interests, and abilities of each student. Instead of a one-size-fits-all model, blended learning allows for differentiation and personalized learning paths.
- Self-Paced Learning: Students can progress at their own speed, moving quickly through topics they grasp and spending more time on those that require additional attention.
- Autonomy: The student-centered approach fosters independent learning, where students take responsibility for their education and become active participants in their learning process.
- Variety of Resources: With access to a wide range of digital tools, students can choose resources that suit their learning style, whether it’s videos, articles, or interactive games.
This approach empowers students, making them feel more in control of their educational experience, which can lead to better engagement and motivation.
Types of Blended Learning Models
Blended learning can be implemented in various ways, depending on the educational goals and the needs of the students. Several models have emerged that showcase different approaches to combining online and face-to-face learning.
Rotation Model
In the Rotation Model, students rotate between different learning stations, which may include online learning, group work, and face-to-face instruction. This model allows for a structured schedule where students experience different learning modalities.
- Station Rotation: Students move between various learning activities within the classroom, such as working on a computer, collaborating with peers, and participating in teacher-led instruction.
- Lab Rotation: Students rotate between different locations, such as a classroom and a computer lab, to access various resources.
- Flipped Classroom: In this variation, students complete online lessons at home and use classroom time for activities like discussions or problem-solving with the teacher.
This model ensures that students are exposed to a variety of learning methods, catering to different preferences and enhancing overall comprehension.
Flex Model
The Flex Model provides students with more autonomy by allowing them to access lessons online while receiving occasional in-person support from their teachers. In this model, the online component is the primary delivery method, and face-to-face instruction is available as needed.
- Self-Directed Learning: Students primarily work through digital lessons at their own pace, seeking help from teachers when required.
- Customizable Support: Teachers act as facilitators, offering one-on-one assistance or small group instruction for students who need additional guidance.
- Flexible Scheduling: This model offers flexibility in terms of when and how students engage with the material, making it suitable for non-traditional learners or those with scheduling constraints.
The Flex Model is ideal for students who are comfortable with independent study but still require occasional interaction with their instructors.
A La Carte Model
The A La Carte Model allows students to take certain courses entirely online while attending other classes in person. This model is particularly common in higher education, where students might prefer to take some subjects in a more flexible, online format while participating in traditional courses for others.
- Course Selection: Students have the freedom to choose which subjects they want to pursue online, allowing for greater flexibility in managing their workload.
- Hybrid Learning: By mixing online and in-person courses, students can benefit from the advantages of both formats.
- Adaptability: This model accommodates diverse learning preferences, making it easier for students to find a balance that suits their individual needs.
The A La Carte Model offers a customizable learning experience, helping students tailor their education to their interests and schedule.
Enriched Virtual Model
In the Enriched Virtual Model, students complete the majority of their coursework online but are required to attend in-person sessions at specific intervals. These sessions typically focus on hands-on activities or group discussions that complement the online material.
- Online-First: The bulk of the learning takes place through digital platforms, with students working independently at their own pace.
- Scheduled Face-to-Face Time: Periodic meetings with teachers and classmates ensure that students receive the benefits of both online and in-person learning.
- Balanced Approach: This model offers the best of both worlds, combining the flexibility of online learning with the social and interactive aspects of face-to-face education.
The Enriched Virtual Model is particularly effective for students who thrive in online environments but still need some personal interaction to reinforce their learning.
Benefits of Blended Learning
Blended learning offers numerous advantages that can enhance the educational experience for students and teachers alike. Its flexibility, personalized approach, and use of technology contribute to its growing popularity in various educational settings.
Flexibility in Learning Pace
One of the key benefits of blended learning is the flexibility it provides in terms of pace. Students can move through the material at a speed that suits their learning style and ability.
- Self-Paced Learning: Students are not confined to the pace of a traditional classroom and can spend more time on challenging concepts or move quickly through familiar topics.
- Time Management: The flexibility allows students to manage their time more effectively, balancing academic responsibilities with extracurricular activities or part-time jobs.
This freedom to control their learning pace can lead to improved retention and a deeper understanding of the material.
Personalized Learning Experiences
Blended learning creates opportunities for personalized instruction, where students receive content that is tailored to their individual needs and preferences.
- Customized Lessons: Teachers can use data-driven insights from online platforms to identify areas where students need extra support and provide targeted resources.
- Choice in Learning Style: Students can choose the learning methods that best suit them, whether it’s watching videos, reading articles, or engaging in interactive simulations.
This personalized approach ensures that students are more engaged and motivated, as the content is relevant to their individual learning journey.
Increased Student Engagement
Blended learning often leads to higher levels of engagement as it incorporates a variety of instructional methods that keep students interested and motivated.
- Interactive Tools: Online platforms offer interactive tools such as quizzes, games, and discussion boards that encourage active participation.
- Collaborative Learning: Students have more opportunities to work together on projects, both in-person and online, fostering a sense of community and teamwork.
The diverse methods of content delivery help maintain student interest and make learning more enjoyable.
Efficient Use of Resources
Blended learning allows for the efficient use of educational resources, making it a cost-effective and scalable option for many institutions.
- Reduced Costs: Schools and universities can save on physical resources such as textbooks and classroom materials by utilizing digital resources.
- Wider Access: Digital platforms allow schools to reach more students, including those in remote or underserved areas, expanding educational opportunities.
By leveraging both online and offline resources, blended learning provides a more sustainable and inclusive educational experience.
Challenges in Blended Learning Implementation
Despite its many benefits, blended learning also comes with challenges that need to be addressed to ensure its successful implementation.
Access to Technology
A significant challenge is ensuring that all students have equal access to technology. In blended learning, students rely heavily on digital devices and internet access to engage with online materials.
- Digital Divide: Not all students have access to reliable internet or devices at home, creating a disparity in learning opportunities.
- Infrastructure Issues: Schools in rural or low-income areas may lack the technological infrastructure needed to support blended learning programs.
Addressing these disparities is essential to creating an equitable learning environment.
Teacher Training and Adaptation
Blended learning requires educators to adopt new teaching methods and become proficient with digital tools. This shift can be challenging for teachers who are accustomed to traditional classroom instruction.
- Professional Development: Schools need to invest in ongoing teacher training to ensure educators can effectively implement blended learning models.
- Adapting to Technology: Teachers may struggle with learning and using new software, which can slow down the integration process.
Without proper training and support, educators may find it difficult to transition to a blended learning environment.
Maintaining Student Motivation
While blended learning offers many benefits, it can also pose challenges in terms of keeping students motivated and engaged.
- Lack of Accountability: Students may struggle with the self-discipline needed to complete online tasks without direct supervision.
- Isolation: The online component can make some students feel disconnected from their peers and teachers, leading to a decrease in motivation.
Blended Learning in Different Educational Levels
Blended learning can be tailored to suit different educational levels, from primary schools to higher education institutions. Each level requires unique approaches and adjustments to ensure that both students and teachers can maximize the benefits of this model.
Application in Primary Education
In primary education, blended learning focuses on creating a balance between traditional and digital learning methods. Younger students require more guidance, so a strong emphasis on teacher-led instruction is essential.
- Interactive Lessons: Digital tools like educational games and videos help keep young learners engaged.
- Parental Involvement: In primary education, parents play a crucial role in supporting blended learning by helping children with online tasks.
- Structured Learning Environment: Teachers must carefully plan how to integrate online activities into the classroom to ensure students remain focused and productive.
Blended learning at this level aims to introduce students to technology while maintaining the necessary hands-on support from teachers.
Implementation in Secondary Education
In secondary education, blended learning takes on a more flexible approach. Students are typically more independent and can handle a mix of self-paced online learning and face-to-face instruction.
- Digital Tools for Research: Secondary students can use online resources for research projects, gaining valuable skills for future academic work.
- Group Collaboration: Online platforms make it easier for students to collaborate on projects, fostering teamwork and communication skills.
- Varied Instruction Methods: Teachers can provide a combination of in-person lectures, digital assignments, and interactive online modules to suit different learning styles.
Blended learning in secondary schools encourages students to take more responsibility for their education while benefiting from the support of their teachers.
Use in Higher Education
Higher education institutions have widely adopted blended learning due to its flexibility and convenience. University students can benefit from a combination of online coursework and in-person lectures or seminars.
- Online Lectures: Many universities now offer recorded lectures, allowing students to learn at their own pace.
- Virtual Discussions: Online forums and virtual study groups encourage students to engage in deep discussions and debates.
- Self-Directed Learning: Students are expected to take a more independent approach to their learning, using online resources to supplement their classroom experience.
Blended learning is ideal for higher education as it gives students the freedom to manage their schedules while providing access to high-quality educational materials.
Blended Learning and the Role of Teachers
The role of teachers in blended learning is significantly different from that of traditional classroom instruction. Teachers are no longer just content deliverers; they become facilitators and guides in the student’s learning journey.
Teacher as Facilitator
In blended learning, the teacher’s role is to support and guide students rather than simply present information. Teachers help students navigate through digital resources and provide targeted assistance when needed.
- Encouraging Independent Learning: Teachers foster a culture where students take responsibility for their own learning, offering support only when necessary.
- Monitoring Progress: Through digital platforms, teachers can track student progress and intervene if they notice any difficulties.
This shift from being a direct instructor to a learning facilitator allows teachers to focus more on individualized support and personalized feedback.
Importance of Continuous Professional Development
For blended learning to succeed, it is crucial for teachers to receive continuous professional development. As digital tools and technologies evolve, teachers must stay updated to provide the best learning experiences for their students.
- Training on Digital Tools: Schools must invest in training teachers to use the latest educational technologies effectively.
- Adapting Teaching Strategies: Teachers need to adjust their teaching strategies to incorporate both online and face-to-face elements seamlessly.
Ongoing professional development helps teachers become more confident in the blended learning environment, ensuring they can meet the diverse needs of their students.
Blended Learning and Assessment Strategies
Assessment is an essential part of any educational model, and blended learning offers opportunities to implement innovative assessment methods that go beyond traditional tests and quizzes.
Formative Assessments in Blended Learning
Formative assessments are used to provide continuous feedback to students during the learning process. In blended learning, teachers can use a variety of tools to conduct these assessments.
- Online Quizzes: Digital quizzes can be used to check students’ understanding of key concepts in real time.
- Discussion Forums: Teachers can assess students’ participation in online discussions to gauge their level of engagement and understanding.
- Peer Reviews: In some cases, students can evaluate each other’s work online, offering constructive feedback.
Formative assessments in blended learning help students stay on track and allow teachers to make timely adjustments to their instruction.
Digital Tools for Assessing Student Progress
Blended learning provides access to advanced digital tools that make it easier to assess student progress. These tools offer a range of data-driven insights that allow teachers to monitor how well students are performing.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): LMS platforms track students’ activity, including completed assignments, quiz results, and time spent on various tasks.
- Interactive Assessments: Tools such as Kahoot or Google Forms enable teachers to create interactive assessments that provide instant feedback.
These tools provide teachers with real-time data that can be used to tailor instruction and offer additional support when needed.
Combining Traditional and Digital Assessments
In a blended learning environment, it’s important to combine both traditional assessments and digital assessments to get a comprehensive view of a student’s abilities.
- Traditional Exams: Face-to-face exams allow teachers to assess students in a structured environment.
- Online Portfolios: Students can create digital portfolios to showcase their work, providing a more holistic view of their learning journey.
This combination ensures that students are evaluated fairly and can demonstrate their knowledge in multiple ways.
Impact of Blended Learning on Students
Blended learning has a profound impact on students, offering several advantages that can enhance their academic performance and overall learning experience.
Improved Academic Performance
Studies have shown that students in blended learning environments often perform better than those in traditional classrooms. This is due to the personalized approach and the flexibility to learn at their own pace.
- Increased Retention: By allowing students to review materials online, they are more likely to retain information.
- Targeted Support: Teachers can provide more individualized attention to students who are struggling, helping to improve their academic performance.
Blended learning’s combination of face-to-face support and digital resources creates an environment where students can thrive academically.
Development of Independent Learning Skills
Blended learning encourages students to take a more active role in their education. By giving them access to online resources and the flexibility to manage their time, students develop important skills that will serve them throughout their academic careers.
- Time Management: Students learn how to balance their time between online and in-person activities.
- Self-Discipline: The online component of blended learning requires students to stay motivated and complete assignments on their own.
These skills are not only beneficial in school but also prepare students for future success in the workplace.
Encouraging Collaboration and Communication
Blended learning fosters a sense of collaboration among students, whether through online platforms or face-to-face interactions.
- Group Projects: Students can work together on projects both in-person and through digital tools, enhancing their teamwork skills.
- Communication Tools: Online forums and chat features allow students to ask questions, share ideas, and engage in meaningful discussions.
This collaborative environment helps students develop the communication skills they need to succeed in the modern world.
Blended Learning in Special Education
Blended learning can be especially beneficial for students with special needs, as it allows for tailored learning experiences that meet individual requirements.
Tailoring Blended Learning for Diverse Learners
Blended learning can be customized to meet the needs of diverse learners, including those with learning disabilities or other special needs. Teachers can provide additional support through online resources and face-to-face instruction.
- Individualized Learning Plans (ILPs): Teachers can create ILPs that incorporate both online and in-person learning activities to meet the specific needs of each student.
- Assistive Technologies: Digital tools such as text-to-speech software or visual aids help students with disabilities access learning materials more easily.
This approach ensures that all students, regardless of their abilities, can benefit from blended learning.
Benefits for Students with Learning Disabilities
For students with learning disabilities, blended learning offers several advantages, including the ability to learn at their own pace and receive personalized support.
- Reduced Pressure: The flexibility of blended learning allows students to complete assignments without the pressure of keeping up with their peers.
- Additional Resources: Online tools provide students with access to additional resources that can help them understand difficult concepts.
Blended learning gives students with disabilities the opportunity to succeed in a supportive and adaptable environment.
Future of Blended Learning
Blended learning is continually evolving, and the future holds exciting possibilities for both educators and students. As technology advances, blended learning will likely play an even larger role in global education.
Technological Innovations Shaping Blended Learning
Technological advancements are transforming blended learning, making it more accessible and effective.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered tools can provide personalized learning experiences by adapting content to each student’s needs.
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR technology is being integrated into blended learning environments, offering immersive experiences that enhance learning.
These innovations are helping to create more engaging and interactive learning experiences for students.
Expanding Blended Learning in Global Education Systems
Blended learning is becoming a popular choice for educational institutions around the world. Its flexibility and scalability make it an ideal solution for schools and universities in developing countries or regions with limited resources.
- Global Access: Digital platforms allow students from all over the world to access high-quality education, regardless of their location.
- Cost-Effective: Blended learning can reduce costs for schools by minimizing the need for physical materials and infrastructure.
What is…Blended Learning?
FAQs
What is the main purpose of blended learning?
Blended learning aims to provide a flexible and personalized learning environment by combining online resources with face-to-face instruction. This approach encourages students to learn at their own pace while benefiting from the direct support of educators. It also enhances student engagement by offering multiple ways to interact with the content.
How does blended learning benefit students?
Blended learning benefits students by offering a more flexible learning experience. It allows them to access educational materials at any time, revisit complex topics, and work at their own pace. Additionally, the integration of online tools promotes collaboration and communication among peers, leading to a more engaging and interactive learning environment.
What are the challenges of blended learning?
One of the main challenges of blended learning is ensuring equal access to technology. Not all students have reliable internet access or devices to participate in online activities. Another challenge is teacher training, as educators need to adapt to new technologies and instructional methods to implement blended learning effectively.
Is blended learning suitable for all educational levels?
Yes, blended learning can be adapted for various educational levels, from primary schools to higher education. However, the structure and tools used may differ depending on the age group and learning needs of the students. For younger learners, more guidance and direct interaction with teachers may be necessary, while older students can handle more self-directed learning.
Conclusion
Blended learning theory is a forward-thinking approach that combines the strengths of traditional classroom instruction with the advantages of digital learning tools. This model empowers students to take control of their education while benefiting from the expertise and guidance of their teachers. It offers the flexibility needed to accommodate different learning styles and paces.
As the role of technology in education continues to expand, blended learning is likely to become an integral part of future educational models. Its ability to balance in-person and virtual learning makes it a valuable tool in promoting student success across various educational contexts.